Hello, it's Lucía again. Today it's my turn to do the journal, so let's try to do it well!
At the beginning of the class, we have revised the Congress of Vienna and its corresponding scheme we did on Tuesday. The main conclusions are:
– They restored absolutism after the exile of Napoleon to Elba.
– They reorganised de map of Europe. For example, the German Confederation was created, having 39 states, Poland and Finland became part of Russia and Norway, which added to Sweden
– They created the Holy Alliance.
Here you have the map that Paqui uses in class:
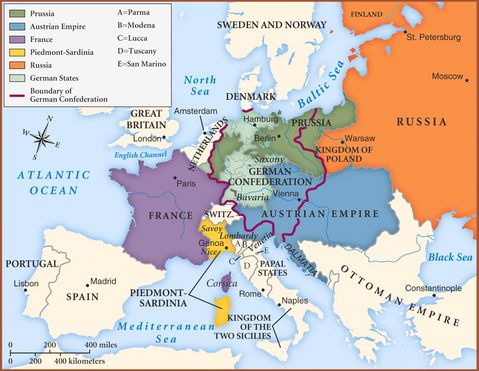 |
| Source: zonu.com |
Later, Paqui has started to explain the creation of two different alliances which had the purpose of defend. The first of them is The Holy Alliance, that I've named before. This alliance was formed by Russia, Austria and Prussia and it tried to preserve absolutism and religion and stop the revolutions in Europe.
But, as the United Kingdom didn't agree with their purposes, they created the Quadruple Alliance, formed by the members of the Holy Alliance plus the United Kingdom; Austria had under its power central Europe, Russia had Eastern Europe and the United Kingdom controlled the seas routes and some islands.
 |
Source: pinterest.com
This photo shows the similarities of the Congress of Vienna and the fall of Napoleon, because when he came back from Elba and the Hundred Days Empire started, the Congress was taking place.
|
But despite these alliances, they couldn't stop the revolutionary ideas so after the Congress two new ideologies spread out.
LIBERALISM:
It’s an ideology that defends that humans are born free and with some rights guaranteed by the State (Social Contract). They agreed with the division of power (but power belonged to the citizens, who chose their representatives). The State couldn't intervene in economy.
The main trends in this ideology were:
– CLASSICAL LIBERALISM: only those who had a good level of wealth or owned properties couldvote (Census Suffrage)
– DEMOCRATIC LIBERALISM: everybody was equal before the law and could vote. (Universal Suffrage).
NATIONALISM:
It defended the right of the nations to decide by themselves and form independent States.
The main two conceptions of nation:
– CONSERVATIVE OR EXCLUDING: they accepted only those who share some common features, like for example language or the "race". (The concept of race in humans doesn't exist, remember this and spread it, please, you're helping to create a better world ♥♥).
– PROGRESSIVE OR INCLUSIVE: they accepted all those who want to belong to the nation, if they accepted its laws.
Unfortunately, the predominant one was (and is) the excluding or conservative.
In the 19th century, several peoples submitted to the big Empires (Russian, Austrian and Ottoman) tried to form independent States based on the conservative or excluding model.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NEW VOCABULARY HERE!
Attend: asistir.
Cape Colony: Colonia del Cabo.
Ceylon: Ceilán.
Quadruple Alliance: Cuádruple Alianza
.
Balance of Powers: equilibrio de poderes.
Threaten: amenaza.
Turncoat: chaquetero
.
Snatch: arrebatar, quitar violentamente.
Trend: tendencia.
Wealth: riqueza.
Classical Liberalism: Liberalismo clásico
.
Democratic Liberalism: Liberalismo radical o democrático.
Self-determination: autodeterminación.
Adress to the German Nation: Discursos de la nación alemana.
AND THAT'S ALL FOLKS! ♥




















